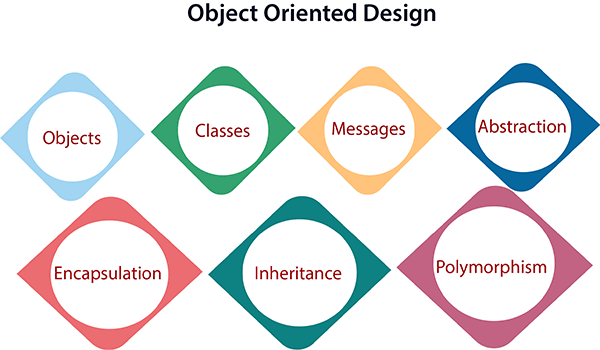
Object oriented design works around the entities and their characteristics instead of functions involved in the software system. This design strategies focuses on entities and its characteristics. The whole concept of software solution revolves around the engaged entities.
Let us see the important concepts of Object Oriented Design:
● Objects – All entities involved in the solution design are known as objects. For example, person, banks, company and customers are treated as objects. Every entity has some attributes associated to it and has some methods to perform on the attributes.
● Classes – A class is a generalized description of an object. An object is an instance of a class. Class defines all the attributes, which an object can have and methods, which defines the functionality of the object.
● In the solution design, attributes are stored as variables and functionalities are defined by means of methods or procedures.
● Encapsulation – In OOD, the attributes (data variables) and methods (operation on the data) are bundled together is called encapsulation. Encapsulation not only bundles important information of an object together, but also restricts access of the data and methods from the outside world. This is called information hiding.
● Inheritance – OOD allows similar classes to stack up in hierarchical manner where the lower or sub-classes can import, implement and re-use allowed variables and methods from their immediate super classes. This property of OOD is known as inheritance. This makes it easier to define specific class and to create generalized classes from specific ones.
● Polymorphism – OOD languages provide a mechanism where methods performing similar tasks but vary in arguments, can be assigned same name. This is called polymorphism, which allows a single interface performing tasks for different types. Depending upon how the function is invoked, respective portion of the code gets executed.