Agile vs. Waterfall: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
In the dynamic world of project management, two methodologies stand out for their distinct approaches to delivering results: Agile and Waterfall. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of projects. Understanding these methodologies is crucial for project managers, teams, and stakeholders who want to optimize their processes and achieve successful outcomes.
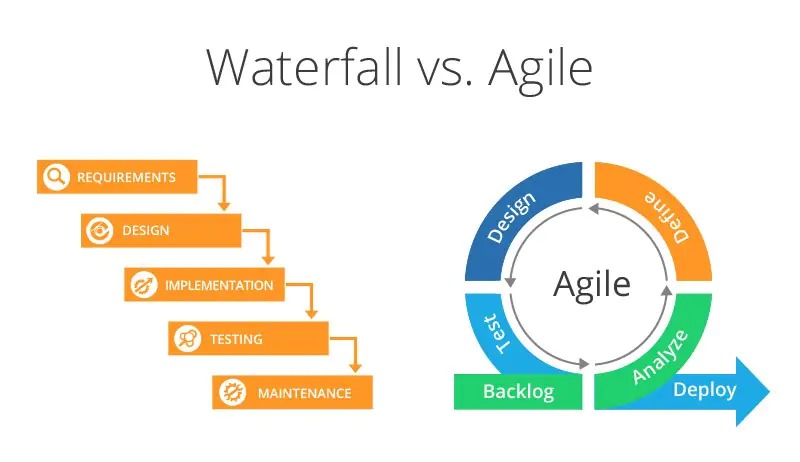
What is Waterfall?
The Waterfall model is one of the oldest project management methodologies, characterized by its linear and sequential design. In this approach, each phase must be completed before the next one begins. The typical stages include:
The Waterfall model is often favored for projects with well-defined requirements and a clear scope, such as construction or manufacturing projects. Its structured approach makes it easier to measure progress and manage timelines. However, its rigidity can be a disadvantage in environments where change is inevitable.
What is Agile?
Agile, on the other hand, is a more flexible and iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and adaptability. Unlike Waterfall, Agile allows teams to work in short cycles, known as sprints, where they plan, develop, and review their work in manageable increments. The key principles of Agile include:
Agile is particularly beneficial in software development and other tech-driven industries, where requirements can change rapidly due to market demands or technological advancements.
Comparing Agile and Waterfall
Flexibility vs. Structure
One of the most significant differences between Agile and Waterfall is flexibility. Agile allows for continuous changes and adaptations, while Waterfall requires a strict adherence to the initial plan. This rigidity can be beneficial for projects with clear, unchanging requirements, but it can hinder responsiveness in rapidly evolving fields.
Customer Involvement
In Agile, customer involvement is integral throughout the project lifecycle. This ongoing feedback loop helps teams create products that truly align with user needs. Conversely, Waterfall typically involves the customer only at the beginning (requirements gathering) and end (final product delivery), which can lead to misaligned expectations and dissatisfaction.
Timeframes and Deliverables
Waterfall projects often work towards a single deliverable at the end of the timeline, making it easier to set deadlines and budgets. Agile projects, however, deliver smaller, incremental updates, allowing for faster adjustments based on feedback and changing priorities.
Risk Management
Agile inherently manages risk through its iterative approach. Each sprint acts as a checkpoint, allowing teams to identify potential issues early. Waterfall, on the other hand, may face significant risks if problems arise late in the project, as changes can be costly and time-consuming to implement.
Conclusion
Choosing between Agile and Waterfall ultimately depends on the nature of your project, the level of uncertainty in your requirements, and your team’s ability to adapt. For projects with stable requirements and a clear end goal, Waterfall might be the best choice. However, for projects that demand flexibility and constant stakeholder engagement, Agile often proves to be more effective.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each methodology will empower project managers to make informed decisions that lead to successful project outcomes.
**